Remember when Bitcoin changed the way we send money without needing a bank? That was just the beginning. Blockchain 1.0 is the technology behind Bitcoin, and it’s reshaping how we handle transactions and share information online. Let’s break down what Blockchain 1.0 is, how it works, and why it’s important for everyone.
1. Why Traditional Transactions Are Outdated
Think about the last time you sent money internationally. It probably took a few days and included unexpected fees, right? That’s because traditional transactions go through banks, which have several downsides:
- High Fees: Each step costs money.
- Slow Processing: Transfers can take days.
- Security Risks: Centralized databases are targets for hackers.
Blockchain 1.0 aims to solve these problems. It offers a faster, cheaper, and more secure way to handle transactions. Think of it like booking a ride with Uber instead of a traditional taxi service direct, fast, and with clear fees.

2. What is Blockchain 1.0, and Why Should You Care?
Blockchain 1.0 works like a digital ledger an open, unchangeable record that everyone can access. It gained fame through Bitcoin, the first major use of this technology. Before blockchain, transactions were controlled by banks, leading to high fees, slow processing times, and potential security risks.
Why Does Blockchain 1.0 Matter to You?
Blockchain 1.0 eliminates middlemen like banks, enabling direct, peer-to-peer transactions. This makes transfers faster, cheaper, and more secure.
Think of it like a shared Google Doc: everyone can view updates, but no one can change anything without everyone else knowing. This openness fosters trust and nearly eliminates the risk of fraud.
3. Inside Blockchain 1.0: How It Really Works
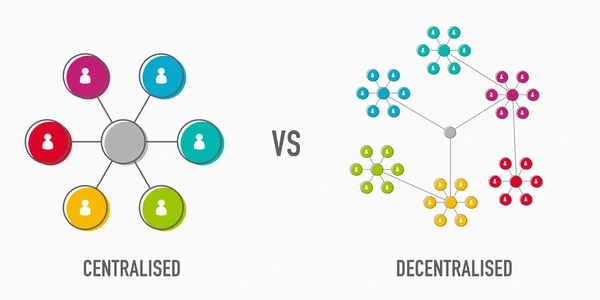
3.1 Peer-to-Peer Networks: Ditching the Middleman
Picture a large Telegram group where every member can see every message, and everyone keeps their own record. If someone shares false information, the rest can quickly spot and correct it. This shared responsibility keeps everything accurate and trustworthy.
Similarly, in a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, transactions happen directly between users. Each participant, or “node,” has their own copy of the blockchain, ensuring there is no single point of failure. This keeps the network secure and reliable.

3.2 Proof of Work (PoW): Keeping Things Honest
Think of social media platforms that rely on multiple people to review content to keep things fair. Blockchain uses a similar method called Proof of Work (PoW) to maintain its security.
Here’s how it works: Miners use powerful computers to solve complex puzzles. The first to solve the puzzle adds a new block of transactions to the blockchain and earns a reward. Before this block is added, other miners check the solution to ensure it’s correct, which helps keep the blockchain secure and accurate.

4. The Perks of Blockchain 1.0: Why It’s a Game-Changer
Blockchain 1.0 brings several advantages:
- No Middlemen: Reduces fees and speeds up transactions.
- High Security: It’s almost impossible to alter the records due to strong cryptographic protections.
- Transparency: Every transaction is visible to everyone on the network.
- Lower Fraud Risk: Decentralization makes fraud more difficult.

5. The Limitations of Blockchain 1.0: What You Should Know…
Despite its benefits, Blockchain 1.0 has some limitations:
- Scalability Issues: It can handle only a limited number of transactions, causing slowdowns during high usage.
- Energy Consumption: Mining requires significant computing power, leading to high energy use.
- Basic Functions: It works well for simple transactions but struggles with more complex operations.
Just like streaming platforms need upgrades to handle big events smoothly, Blockchain 1.0 needs improvements to manage more transactions efficiently. This is where Blockchain 2.0 comes in, offering better solutions to these challenges.
Conclusion: What’s Next for Blockchain?
Blockchain 1.0 has already revolutionized digital transactions, making them more secure, transparent, and decentralized. But this is just the beginning. With Blockchain 2.0 and beyond, new possibilities like smart contracts and decentralized apps (dApps) are emerging. Curious about how blockchain will continue to evolve? Stay tuned the journey is just getting started.